The power of white space in product design
If you overhear a design QA session between a product designer and an engineer, odds are you’ll hear the product designer say something like this:
“Can you add 8 pixels of padding here and also there? … Actually, let’s make it 16 pixels.”
So, why are product designers so picky about padding?
Padding, also known as white space, is the empty space between and around individual elements of a page layout; these elements could be pieces of copy, images, cards, buttons, icons, etc. When used correctly, white space brings visual clarity and balance to a layout.
Think of white space as a breath of fresh air. Just as humans need air to breathe, designs need white space to breathe. Yes, this may sound corny. But I stand by this.
An example of white space usage
Using Wayfair as an example, the product design team follows a strict padding rule to ensure consistency and easy maintenance across site. This rule is embedded into their design toolkit, a collection of user interface design elements that are the building blocks for all of the site designs. The rule states that the spacing between every design element should be a multiple of 8 pixels; this means that the spacing could be 8, 16, 24, 32, 40 pixels and so on. This rule brings intentionality to the use of white space and creates visual consistency across the site experience.
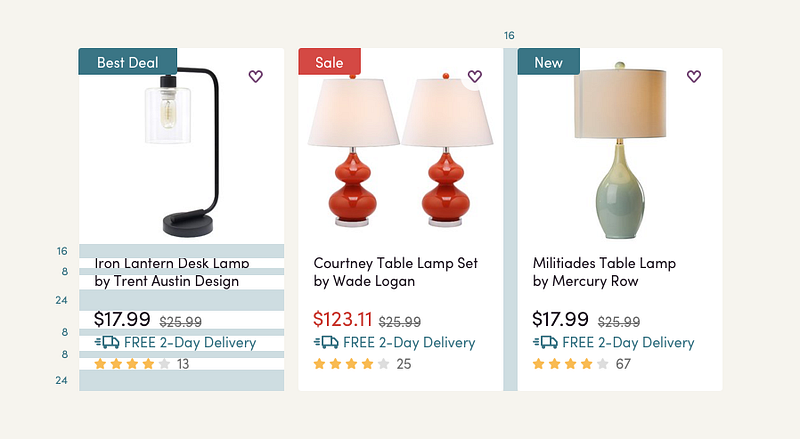 “Rule of 8” in action
“Rule of 8” in action
How can white space improve the user experience?
It helps maintain focus
White space is a tool that helps guide the user experience. We use white space to create focus points for our users drawing their attention to certain elements. The greater the padding around a particular element on a page, the greater the emphasis on that element. In the example below, focus is clearly maintained on the call to action and the primary messaging.
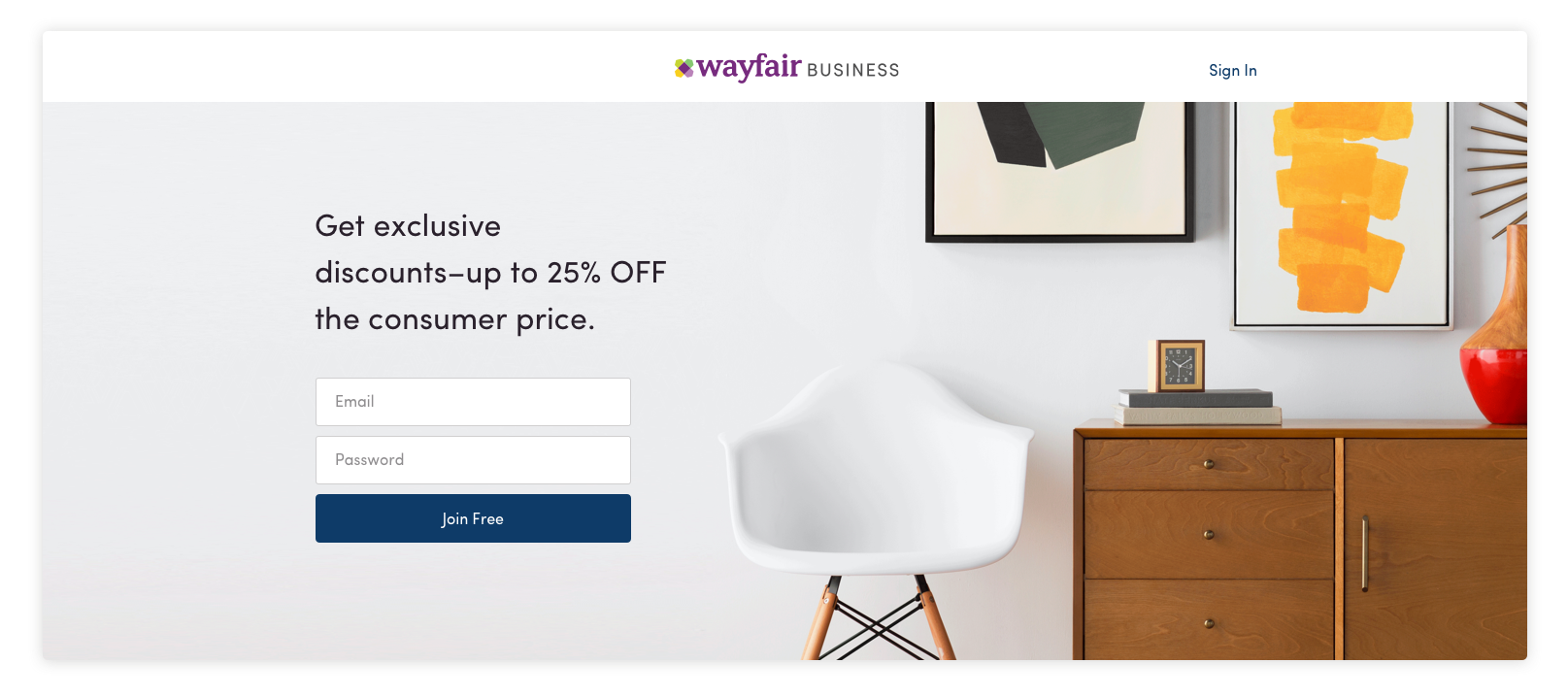 Aaaah, drink in all that white space
Aaaah, drink in all that white space
Unfortunately, we do not always have the luxury of this kind of white space. This is a rarity, so enjoy it while it lasts. On a typical e-commerce page, a product designer is faced with the challenge of balancing multiple calls to action, secondary links, imagery, pieces of copy—the list goes on. The example below showcases our product details page (PDP), a page that demands a lot from our user. Strategically placed white space helps our user navigate the visual noise on this page and potentially increases conversion.
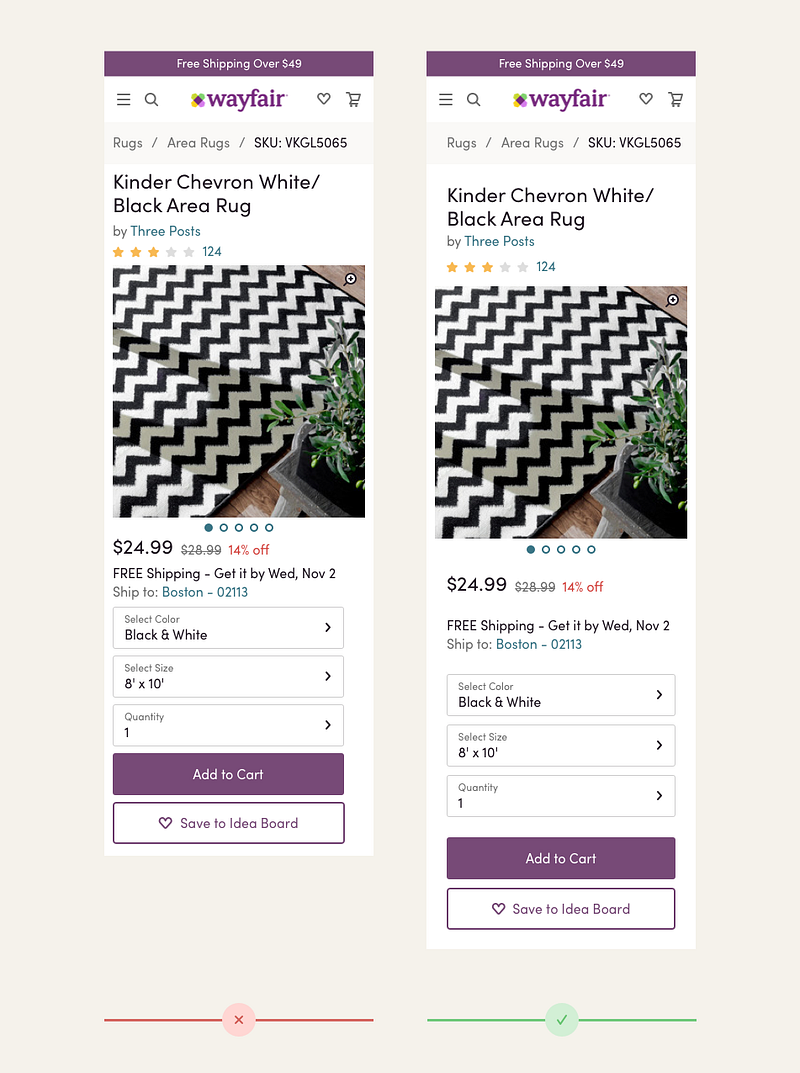 White space helps focus the user on each interaction area on the PDP
White space helps focus the user on each interaction area on the PDP
It improves visual organization
In addition to highlighting areas of focus, white space plays a huge role in the visual organization of a page. White space is essential to clarifying relationships and separating sections with different purposes; it is also the driving force behind the Gestalt Principle of Proximity, which states:
Objects or shapes that are close to one another appear to form groups.
Clearly defining different parts of a page increases our user’s confidence in the site experience; forcing our user to think through a confusing layout is something every product designer wants to avoid. The following example showcases Wayfair’s homepage, a page that could easily appear overwhelming if white space was not used properly.
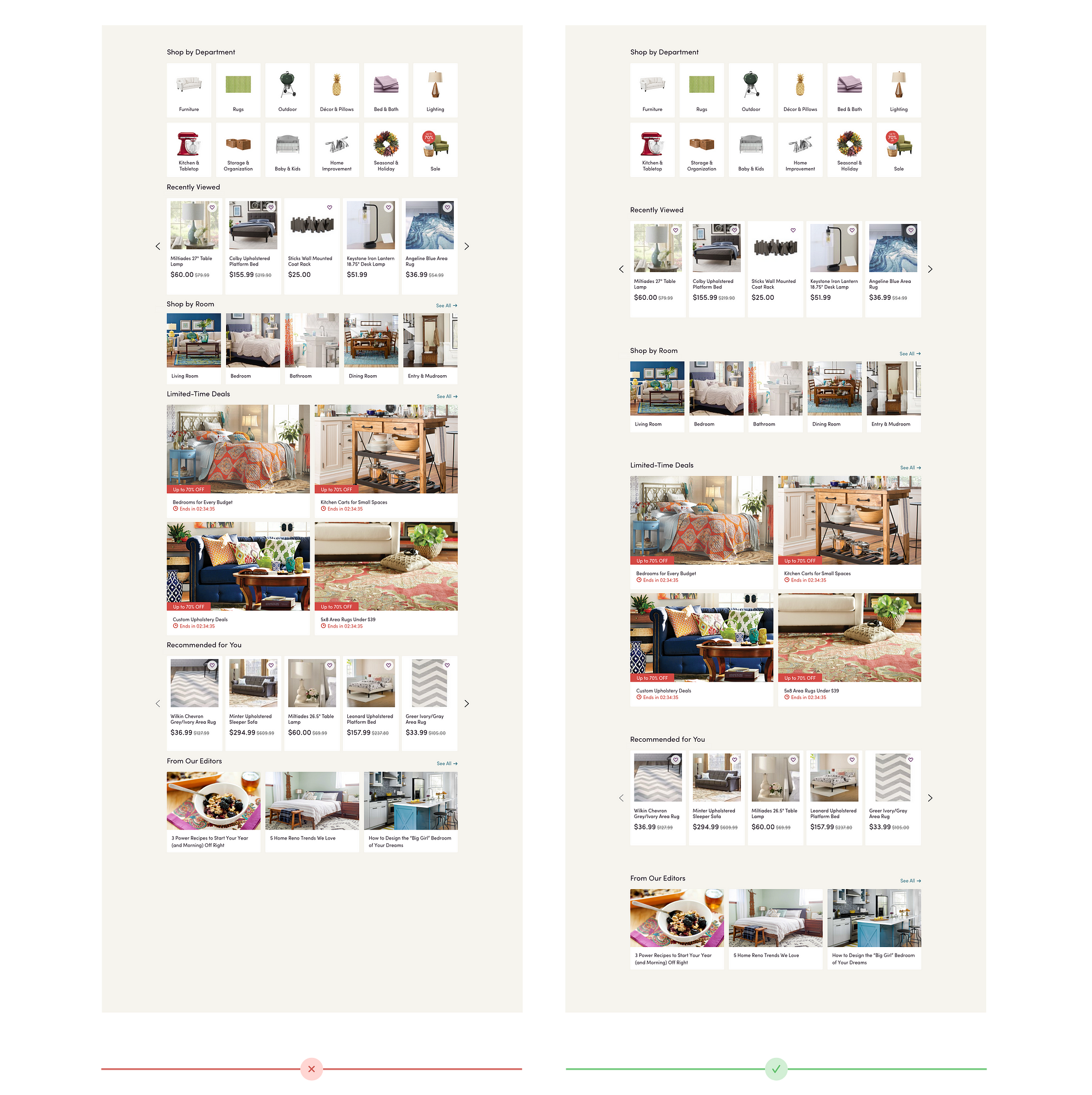 White space clearly defines the different sections on Wayfair’s homepage
White space clearly defines the different sections on Wayfair’s homepage
It increases readability
In addition to defining the organization of a page, white space can greatly improve the readability of a page. It’s important to be mindful about the spacing between lines of copy—and even letters—as thoughtful spacing will make it easier for the user to digest. More spacing is generally better, but too much could potentially make lines of copy feel disconnected. It’s all about finding the right balance.
What are common concerns around white space?
“White space is wasted space!”
This is a myth. White space is not wasted space. There is a tendency for some of our stakeholders to fill white space with more content when it is not always necessary. Everyone has heard the saying “less is more”. This applies to content on any given page, where less visual noise makes for a better user experience. On Wayfair’s checkout flow (seen below), the white space underneath the main call to action may be vast but it beautifully balances and supports the elements on this page.
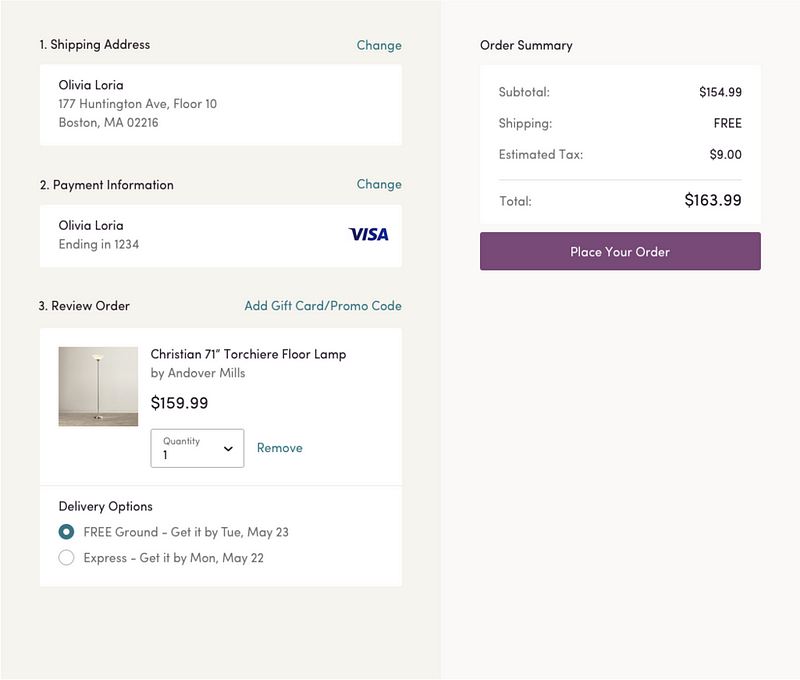 Large areas of white space do NOT need to be filled with content
Large areas of white space do NOT need to be filled with content
“White space pushes content below the fold and users will not see this content!”
Users will scroll and scroll some more. I promise you. There is this myth that users will not always scroll to see all the content on a page. Thus, some of our stakeholders request that the majority of a page’s content lives above the fold.
Users have evolved and become more comfortable with scrolling. There are definitely certain elements that are best suited above the fold, but it’s important not to limit the use of white space to accommodate for the fold.
Conclusion
Every product designer wants to design the best possible user experience; with this in mind, white space is a powerful tool that can help achieve this from a user interface perspective. It should be heavily integrated into the design process .
Think you’re using too much white space? There’s a good chance you’re not. If anything, you’re probably not using enough. When in doubt, add more white space…